Or, it could use its earnings to reduce liabilities, which would also result in an increase in its common equity and BVPS. Another way to increase BVPS is to repurchase common stock from shareholders and many companies use earnings to buy back shares. It may not include intangible assets such as patents, intellectual property, brand value, and goodwill. It also may not fully account for workers’ skills, human capital, and future profits and growth. Therefore, the market value — which is determined by the market (sellers and buyers) and is how much investors are willing to pay by accounting for all of these factors — will generally be higher.

On the balance sheet, you see “Total Stockholders’ Equity” with a value of $138.2 billion. This figure is calculated by adding the values of preferred stock, common stock, Treasuries, paid-in capital, additional comprehensive income, and retained earnings. For value investors, book value is the sum of the amounts of all the line items in the shareholders’ equity section on a company’s balance sheet. You can also calculate book value by subtracting a business’s total liabilities from its total assets.
What Does a Price-to-Book (P/B) Ratio of 1.0 Mean?
This figure represents the minimum value of a company’s equity and measures the book value of a firm on a per-share basis. Breaking down the book value on a per-share may help investors decide whether they think the stock’s market value is overpriced or underpriced. Nevertheless, most companies with expectations to grow and produce profits in the future will have a book value of equity per share lower than their current publicly traded market share price. Book value per share is just one of the methods for comparison in valuing of a company. Enterprise value, or firm value,
market value, market capitalization, and other methods may be used in different circumstances or compared to one
another for contrast.
- This differs from book value for investors because it is used internally for managerial accounting purposes.
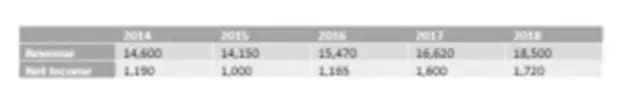
- By multiplying the diluted share count of 1.4bn by the corresponding share price for the year, we can calculate the market capitalization for each year.
- So, if the company’s shares had a current market value of $13.17, its price-to-book ratio would be 1.25 ($13.17 ÷ $10.50).
- If the firm’s BVPS increases, the stock should be perceived as more valuable, and the stock price should increase.
- An exception to this valuation is in bank stocks which tend to trade below their BVPS due to their increased risk from trading activities.
Price-to-book (P/B) ratio as a valuation multiple is useful for comparing value between similar companies within the same industry when they follow a uniform accounting method for asset valuation. The ratio may not serve as a valid valuation basis when comparing companies from different sectors and industries because companies record their assets differently. However, if this builds brand value and the company is able to charge premium prices for its products, its stock price might rise far above its BVPS. It’s important to use the average number of outstanding shares in this calculation.
Book Value Per Share (BVPS): Definition, Formula, How to Calculate, and Example
Investors must compare the BVPS to the market price of the stock to begin to analyze how it impacts them. In return, the accumulation of earnings could be used to reduce liabilities, which leads to higher book value of equity (and BVPS). Comparing BVPS to the market price of a stock is known as the market-to-book ratio, or the price-to-book ratio.

With those three assumptions, we can calculate the book value of equity as $1.6bn. If relevant, the value of preferred equity claims should also be subtracted from the numerator, the book value of equity. Book value gets its name from accounting lingo, where the accounting journal and ledger are known as a company’s “books.” In fact, another name for accounting is bookkeeping. As a result, a high P/B ratio would not necessarily be a premium valuation, and conversely, a low P/B ratio would not automatically be a discount valuation.
Concept of Book Value per Share
They may generate sales with that software, but there isn’t a warehouse full of software code that investors can look at to gauge future sales. For companies seeking to increase their book value of equity per share (BVPS), profitable reinvestments can lead to more cash. In other words, investors understand the company’s recent performance is underwhelming, but the potential for a long-term turnaround and the rock-bottom price can create a compelling margin of safety. For example, if a company has a total asset balance of $40mm and liabilities of $25mm, then the book value of equity is $15mm.
The Formula for Book Value Per Common Share Is:
Stock repurchases occur at current stock prices, which can result in a significant reduction in a company’s book value per common share. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy more assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases. If, for example, the company generates $500,000 in earnings and uses $200,000 of the profits to buy assets, common equity increases along with BVPS. On the other hand, if XYZ uses $300,000 of the earnings to reduce liabilities, common equity also increases. Book value per common share (or, simply book value per share – BVPS) is a method to calculate the per-share book value of a company based on common shareholders’ equity in the company. The book value of a company is the difference between that company’s total assets and total liabilities, and not its share price in the market.
Book value is the value of a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities. Value investors look for companies with relatively low book values (using metrics like P/B ratio or BVPS) but otherwise strong fundamentals as potentially underpriced stocks in which to invest. The market value per share is a company’s current stock price, and it reflects a value that market participants are willing to pay for its common share. The book value per share is calculated using historical costs, but the market value per share is a forward-looking metric that takes into account a company’s earning power in the future.
Should the company dissolve, the book value per common share indicates the dollar value remaining for common shareholders after all assets are liquidated and all creditors are paid. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance.
