Market Value Definition & ExampleIn simplified terms, it’s also the original value of the common stock issued plus retained earnings, minus dividends and stock buybacks. BVPS is the book value of the company divided by the corporation’s issued and outstanding common shares. This is simply the tangible asset value divided by the number of outstanding shares when a business is a corporation.
How do you find the book value of an asset?
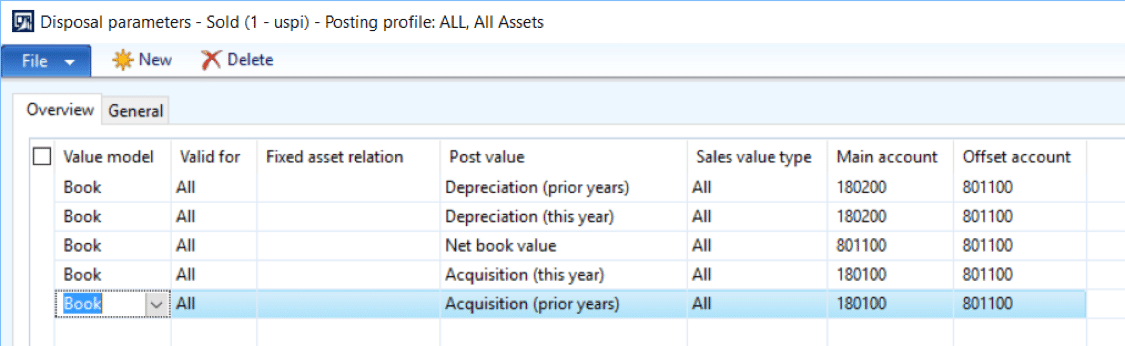
book value of an asset definition. The book value of an asset is the asset’s cost minus the accumulated depreciation since the asset was acquired. This net amount is not an indication of the asset’s fair market value. The book value of an asset is also referred to as the asset’s carrying value.
Related wikiHows
For example, if Company XYZ has total assets of $100 million and total liabilities of $80 million, the book value of the company is $20 million. In a very broad sense, this means that if the company sold off its assets and paid down its liabilities, the equity value or net worth of the business, would be $20 million. A good measure of the value of a stockholder’s residual claim at any given point in time is the book value of equity per share (BVPS). Book value is the accounting value of the company’s assets less all claims senior to common equity (such as the company’s liabilities).If a company’s share price falls below its BVPS a corporate raider could make a risk-free profit by buying the company and liquidating it. If book value is negative, where a company’s liabilities exceed its assets, this is known as a balance sheet insolvency. For example, real estate owned by a company may gain in market value at times, while its old machinery can lose value in the market because of technological advancements. In these instances, book value at the historical cost would distort an asset or a company’s true value, given its fair market price.For quite legitimate reasons, your company may list items like goodwill as assets on the balance sheet. Then, there’s the fact that a firm’s stock may be valued by investors at a price that is significantly different than the book value, or equity, per share. Tangible asset value is a measure of a company’s worth that focuses on the property the firm actually owns.You simply need to look at Coca-Cola’s income statement to understand why. In other words, it makes at least 15 cents of profit from each dollar of sales. The takeaway is that Coca-Cola has very valuable assets – brands, distribution channels, beverages – that allow the company to make a lot of money each year. Because these assets are so valuable, the market values them far more than what they are stated as being worth from an accounting standpoint. The book value of a company is important for accounting purposes, and it’s part of the review of the business if the business is to be sold.

For example, if the company has 100,000 shares outstanding and tangible asset value of $1.4 million, the TAV per share equals $14. Note that this is a smaller figure than the book value per share, which is equal to shareholder’s equity, including intangible assets, divided by the number of shares outstanding. In a broad sense, this means that if the company sold off its assets and paid down its liabilities, the equity value ornet worthof the business would be $20 million. The Coca-Cola Co. has historically traded at a P/B ratio of 4 to 5.
What is book value of fixed assets?
An asset’s book value is equal to its carrying value on the balance sheet, and companies calculate it netting the asset against its accumulated depreciation. Book value can also be thought of as the net asset value of a company calculated as total assets minus intangible assets (patents, goodwill) and liabilities.
Book Value vs. Carrying Value: What Is the Difference?
Book value simply implies the value of the company on its books, often referred to as accounting value. It’s the accounting value once assets and liabilities have been accounted for by a company’s auditors.
Why market value is important
- Book Value literally means the value of the business according to its “books” or financial statements.
- For example, if Company XYZ has total assets of $100 million and total liabilities of $80 million, the book value of the company is $20 million.
- In this case, book value is calculated from the balance sheet, and it is the difference between a company’s total assets and total liabilities.
Since book value isn’t related to the market value of an individual asset, it can be used as a reference point, but not as a selling price. Market value of equity is the total dollar value of a company’s equity calculated by multiplying the current stock price by total outstanding shares.
Understanding Book Value
What we’re looking for is the number of shares outstanding, not simply issued. The two numbers can be different, usually because the issuer has been buying back its own stock. In this case, the shares outstanding number is stated at 3.36 billion, so our BVPS number is $71.3 billion divided by 3.36 billion, which equals $21.22. Each share of common stock has a book value – or residual claim value – of $21.22. At the time Walmart’s 10-K for 2012 came out, the stock was trading in the $61 range, so the P/BVPS multiple at that time was around 2.9 times.
The difference between book value and market value
To calculate tangible book value, we must subtract the balance sheet value of intangibles from common equity and then divide the result by shares outstanding. To continue with the Walmart example, the value of goodwill on the balance sheet is $20.6 billion (we are assuming the only intangible asset material to this analysis is goodwill). The price/TBVPS ratio is around 4 times when Walmart’s K is released. Again, we would want to examine the trend in the ratio over time and compare it to similar companies to assess relative value.For example, Walmart’s January 30, 2012 balance sheet indicates that shareholders’ equity has a value of $71.3 billion. The number is clearly stated as a subtotal in the equity section of the balance sheet. To calculate BVPS, you need to find the number of shares outstanding, which is also usually stated parenthetically next to the common stock label (on Yahoo! Finance, it’s located in Key Statistics).
What is Book Value?
Keep in mind that book value and BVPS do not consider the future prospects of the firm – they are only snapshots of the common equity claim at any given point in time. Deriving the book value of a company is straightforward since companies report total assets and total liabilities on their balance sheet on a quarterly and annual basis. Additionally, the book value is also available asshareholders’ equity on the balance sheet. The book value of equity per share (BVPS) metric can be used by investors to gauge whether a stock price is undervalued, by comparing it to the firm’s market value per share.Book Value literally means the value of the business according to its “books” or financial statements. In this case, book value is calculated from the balance sheet, and it is the difference between a company’s total assets and total liabilities.Another way to increase BVPS is to repurchase common stock from shareholders. Using the XYZ example, assume that the firm repurchases 200,000 shares of stock and that 800,000 shares remain outstanding. If common equity is $10 million, BVPS increases to $12.50 per share. Besides stock repurchases, a company can also increase BVPS by taking steps to increase the asset balance and reduce liabilities. If XYZ can generate higher profits and use those profits to buy more assets or reduce liabilities, the firm’s common equity increases.
How to Find the Value of Old Books
This means that Coca-Cola’s market value has typically been 4 to 5 times larger than the stated book value as seen on the balance sheet. In other words, the market values the firm’s business as being significantly worth more than the company’s value on its books.Whether book value is an accurate assessment of a company’s value is determined by stock market investors who buy and sell the stock. Market value has a more meaningful implication in the sense that it is the price you have to pay to own a part of the business regardless of what book value is stated. The term book value derives from the accounting practice of recording asset value at the original historical cost in the books. While the book value of an asset may stay the same over time by accounting measurements, the book value of a company collectively can grow from the accumulation of earnings generated through asset use. Equity investors often compare BVPS to the market price of the stock in the form of the market price/BVPS ratio to attribute a measure of relative value to the shares.An even better approach is to assess a company’s tangible book value per share (TBVPS). Tangible book value is the same thing as book value except it excludes the value of intangible assets. Intangible assets, such as goodwill, are assets that you can’t see or touch. Intangible assets have value, just not in the same way that tangible assets do; you cannot easily liquidate them. By calculating tangible book value we might get a step closer to the baseline value of the company.If a company’s BVPS is higher than its market value per share—its current stock price—then the stock is considered undervalued. If the firm’s BVPS increases, the stock should be perceived as more valuable, and the stock price should increase. Book value of equity per share (BVPS) is the ratio of equity available to common shareholders divided by the number of outstanding shares. This figure represents the minimum value of a company’s equity, and measures the book value of a firm on a per-share basis.
