Activity Cost Driver Definition
How Batch-Level Activities Works
Cost pools are commonly used for the allocation of factory overhead to units of production, as required by several accounting frameworks. They are also used in activity-based costing to allocate costs to activities. A business that wants to allocate costs at a highly-refined level may choose to do so using a number of cost pools.The main costs and limitations of an ABC system are the measurements necessary to implement it. ABC systems require management to estimate costs of activity pools and to identify and measure cost drivers to serve as cost allocation bases. Even basic ABC systems require many calculations to determine costs of products and services. Activity-based costing (ABC) is a more accurate way of allocating both direct and indirect costs. ABC calculates the true cost of each product by identifying the amount of resources consumed by a business activity, such as electricity or man hours.In using activity-based costing, the company identified four activities that were important cost drivers and a cost driver used to allocate overhead. These activities were purchasing materials, setting up machines when a new product was started, inspecting products, and operating machines.
What Are the Types of Costs in Cost Accounting?
Look at the overhead rates computed for the four activities in the table below. Note that the total overhead for current year is $2,000,000 using activity-based costing, just as it was using a traditional costing method. The total amount of overhead should be the same whether using activity-based costing or traditional methods of cost allocation to products. The primary difference between activity-based costing and the traditional allocation methods is the amount of detail; particularly, the number of activities used to assign overhead costs to products.

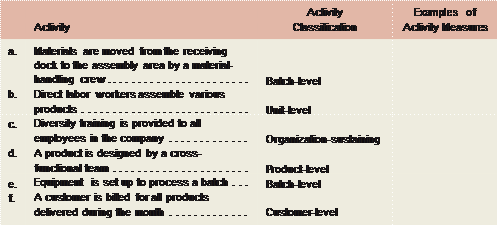
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a system that tallies the costs of overhead activities and assigns those costs to products. Batch-level activities are one of the five broad levels of activity that activity-based costing account for. Each of these levels is assessed by cost, and these costs are allocated to the company’s overhead costs. The other levels of activity that are accounted for by activity-based costing are unit-level activities, customer-level activities, production-level activities, and organization-sustaining activities.When using ABC, the total cost of each activity pool is divided by the total number of units of the activity to determine the cost per unit. Activity-based costing is a system that provides detailed information regarding a company’s production expenditures. Activity-based costing (ABC) is an accounting method that allocates both direct and indirect costs to business activities. In a business organization, the ABC methodology assigns an organization’s resource costs through activities to the products and services provided to its customers.
Four Levels of Activity
Traditional allocation uses just one activity, such as machine-hours. In practice, companies using activity-based costing generally use more than four activities because more than four activities are important. One of the lessons of activity-based costing has been that the more complex the business, the higher the indirect costs.Batch-level activities are work actions that are classified within an activity-based costing accounting system, often used by production companies. Batch-level activities are related to costs that are incurred whenever a batch of a certain product is produced. However, these costs are accounted for regardless of the related production run’s size. Examples of these batch-level cost drivers can often include machine setups, maintenance, purchase orders, and quality tests.Activity-based costing records the costs that traditional cost accounting does not do. Robin Cooper and Robert S. Kaplan, proponents of the Balanced Scorecard, brought notice to these concepts in a number of articles published in Harvard Business Review beginning in 1988. Cooper and Kaplan described ABC as an approach to solve the problems of traditional cost management systems. These traditional costing systems are often unable to determine accurately the actual costs of production and of the costs of related services. Consequently, managers were making decisions based on inaccurate data especially where there are multiple products.Direct labour and materials are relatively easy to trace directly to products, but it is more difficult to directly allocate indirect costs to products. Where products use common resources differently, some sort of weighting is needed in the cost allocation process. The cost driver is a factor that creates or drives the cost of the activity. For the activity of running machinery, the driver is likely to be machine operating hours, looking at labor, maintenance, and power cost during the period of machinery activity. Activity-based costing was later explained in 1999 by Peter F. Drucker in the book Management Challenges of the 21st Century.Analysis More overhead is allocated to the lower volume mountain bicycles using activity-based costing. By failing to assign costs to all of the activities, touring bicycles were subsidizing mountain bicycles. Activity-based costing has revealed that low-volume, specialized products have been the cause of greater costs than managers had realized.
- In activity-based costing (ABC), an activity cost driver influences the costs of labor, maintenance, or other variable costs.
- Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing method that assigns overhead and indirect costs to related products and services.
- Cost drivers are essential in ABC, a branch of managerial accounting that allocates the indirect costs, or overheads, of an activity.

Product-Based Costs
For example, the cost of service departments can be allocated to production departments using the direct method. Also the cost hierarchy can be used to help establish cost pools and identify cost drivers used to allocate costs. Organizations are also concerned with measuring and reducing the cost of quality by categorizing quality costs into four categories—prevention, appraisal, internal failure, and external failure. Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing method that identifies activities in an organization and assigns the cost of each activity to all products and services according to the actual consumption by each. This model assigns more indirect costs (overhead) into direct costs compared to conventional costing.
What is product level activity?
Batch-level activities are those actions related to a defined cluster of units. The concept is most commonly used in the allocation of overhead costs to production or service activities. A classic example is the cost to set up a production run; this cost is then assigned to the units produced as a result of that setup.In activity-based costing (ABC), an activity cost driver influences the costs of labor, maintenance, or other variable costs. Cost drivers are essential in ABC, a branch of managerial accounting that allocates the indirect costs, or overheads, of an activity. Activity-based costing (ABC) is a costing method that assigns overhead and indirect costs to related products and services. This accounting method of costing recognizes the relationship between costs, overhead activities, and manufactured products, assigning indirect costs to products less arbitrarily than traditional costing methods.
AccountingTools
ABC is generally used as a tool for understanding product and customer cost and profitability based on the production or performing processes. As such, ABC has predominantly been used to support strategic decisions such as pricing, outsourcing, identification and measurement of process improvement initiatives.Imagine that each month you produce 100,000 gallons of vanilla ice cream and your friend produces 100,000 gallons of 39 different flavors of ice cream. Further, assume your ice cream is sold only in one liter containers, while your friend sells ice cream in various containers. Your friend has more complicated ordering, storage, product testing (one of the more desirable jobs, nevertheless), and packing in containers.Activity-based costing (ABC) is a method of assigning overhead and indirect costs—such as salaries and utilities—to products and services. Activity‐based costing assumes that the steps or activities that must be followed to manufacture a product are what determine the overhead costs incurred. Each overhead cost, whether variable or fixed, is assigned to a category of costs. Cost drivers are the actual activities that cause the total cost in an activity cost pool to increase. The number of times materials are ordered, the number of production lines in a factory, and the number of shipments made to customers are all examples of activities that impact the costs a company incurs.
Is inspection a batch level activity?
A product-level activity is an action taken in support of a specific product or activity. These actions are taken irrespective of the amount of production or service volume associated with a product. Examples of product-level activities are: Cost of the product manager for a product.
How are period costs and product costs different?
However, some indirect costs, such as management and office staff salaries, are difficult to assign to a product. A number of methods can be used to assist in the cost allocation process.
Activity-Based Costing Activities
For example, direct labor hours are a driver of most activities in product manufacturing. If the cost of labor is high, this will increase the cost of producing all company products or services. If the cost of warehousing is high, this will also increase the expenses incurred for product manufacturing or providing services.
