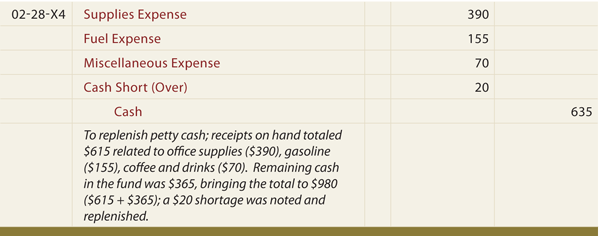
When an individual takes money out of the petty cash fund, he notes it in the petty cash ledger. The purchase can then be made for the business and any money left over can be taken back to the petty cash fund. Petty cash funds are often created by a business owner simply writing a business check to cash.When the fund requires more cash or at the end of an accounting period, the petty cash custodian requests a check for the difference between the cash on hand and the total assigned to the fund. At this time, the person who provides cash to the custodian should examine the vouchers to verify their legitimacy. The transaction that replenishes the petty cash fund is recorded with a compound entry that debits all relevant asset or expense accounts and credits cash. Consider the journal entry below, which is made after the custodian requests $130 to replenish the petty cash fund and submits vouchers that fall into one of three categories.Consider switching to a cash-only budgetto cover all of your other expenses during the month so that you can more closely monitor your spending. And be sure to build up an emergency fund to avoid going into debt when these unexpected expenses occur. A company uses a cash short and over account to balance its accounting records when it replenishes its petty cash account. A petty cash account is an account a company uses to pay for small expenses.
Cash Over Journal Entry
The journal entry on the balance sheet should list a debit to the business bank account and a credit to the petty cash account. When petty cash is used for business expenses, the appropriate expense account — such as office supplies or employee reimbursement — should be expensed. Most companies keep a small amount of cash on hand to pay minor business-related expenses that don’t warrant the writing of a check or use of the corporate credit card.
Example of How the Account Cash Short and Over is Used
Let’s illustrate the Cash Short and Over account with the petty cash fund. Assume that the company has a petty cash fund of $100 and its general ledger account Petty Cash reports an imprest balance of $100. Let’s now assume that when the petty cash fund is replenished, there is $6.00 on hand and there are $93.00 of petty cash vouchers. A petty cash transaction is one in which an employee or business owner takes money out of the petty cash fund for the purpose of buying something for the business.
Cash Over Journal Entry Example
What is cash short and over?
Definition of Cash Short and Over Account The account Cash Short and Over is an income statement account (within a company’s general ledger) in which shortages or overages of cash are recorded. A company to record unexplained differences arising when a company’s petty cash fund is replenished.Cash is money in the form of currency, which includes all bills, coins, and currency notes. A demand deposit is a type of account from which funds may be withdrawn at any time without having to notify the institution. Examples of demand deposit accounts include checking accounts and savings accounts.Cash and cash equivalents help companies with their working capital needs since these liquid assets are used to pay off current liabilities, which are short-term debts and bills. A money market fund is a type of mutual fund that invests in high-quality, short-term debt instruments and cash equivalents. Also called money market mutual funds, money market funds work like any mutual fund.
What to Do When You Are Short on Cash
Exceptions can exist for short-term debt instruments such as Treasury-bills if they’re being used as collateral for an outstanding loan or line of credit. In other words, there can be no restrictions on converting any of the securities listed as cash and cash equivalents. For simplicity, the total value of cash on hand includes items with a similar nature to cash. If a company has cash or cash equivalents, the aggregate of these assets is always shown on the top line of the balance sheet.
Normal Petty Cash Account Balance
- A money market fund is a type of mutual fund that invests in high-quality, short-term debt instruments and cash equivalents.
- Also called money market mutual funds, money market funds work like any mutual fund.
- Cash and cash equivalents help companies with their working capital needs since these liquid assets are used to pay off current liabilities, which are short-term debts and bills.
This is because cash and cash equivalents are current assets, meaning they’re the most liquid of short-term assets. Cash and cash equivalents refers to the line item on the balance sheet that reports the value of a company’s assets that are cash or can be converted into cash immediately. Cash equivalents include bank accounts and marketable securities, which are debt securities with maturities of less than 90 days.
The owner of the business or the manager of the department typically sets the standards for what the money can be used for. The cash ratio—a company’s total cash and cash equivalents divided by its current liabilities—measures a company’s ability to repay its short-term debt. There are some exceptions to short-term assets and current assets being classified as cash and cash equivalents.

In the world of business, a number of miscellaneous expenses can come up on a day-to-day basis. Instead of issuing a purchase order to buy these items, many businesses use a petty cash fund. A petty cash fund is an amount of cash that a business uses to make small, miscellaneous purchases.Cash and cash equivalents information is sometimes used by analysts in comparison to a company’s current liabilities to estimate its ability to pay its bills in the short term. However, such an analysis may be flawed if there are receivables that can be readily converted into cash within a few days. Cash and cash equivalents is a line item on the balance sheet, stating the amount of all cash or other assets that are readily convertible into cash. Any items falling within this definition are classified within the current assets category in the balance sheet.
Is cash short and over a debit or credit?
Debit your cash short and over account in your journal entry by the amount of cash short. This represents an expense. Alternatively, credit your cash short and over account by the amount of cash over. This represents a revenue.The size of a petty cash fund varies depending on the needs of the business. For this reason, companies typically establish a petty cash fund that needs to be replenished every two to four weeks. Money in a petty cash fund can be used for many purposes in the regular operations of a business. For instance, most businesses need to buy random supplies such as postage stamps, envelopes, paper or pens. Some offices use petty cash money to pay for occasional office lunches, parking fees or other expenses that come up throughout the day.However, oftentimes cash equivalents do not include equity or stock holdings because they can fluctuate in value. Companies normally use checks to pay their obligations because checks provide a record of each payment. Companies also maintain a petty cash fund to pay for small, miscellaneous expenditures such as stamps, small delivery charges, or emergency supplies.
The cash over and short account
All demand account balances as of the date of the financial statements are included in cash totals. Companies with a healthy amount of cash and cash equivalents can reflect positively in their ability to meet their short-term debt obligations. Examples of cash equivalents include commercial paper, Treasury bills, and short-term government bonds with a maturity date of three months or less.
Balance Sheet
Marketable securities and money market holdings are considered cash equivalents because they are liquid and not subject to material fluctuations in value. The petty cash account should be reconciled and replenished every month to ensure the account is balanced and any variances are accounted for. The accountant should write a check made out to “Petty Cash” for the amount of expenses paid for with the petty cash that month to bring the account back up to the original amount. The check should be cashed at the company’s bank and the cash placed back in the petty cash safe or lock box. The normal balance of petty cash can vary depending on the size of the company.Typically a small-to-medium business keeps about $100 of cash on hand, but large corporations may have as much as $500, depending on their needs. It is generally not a good idea to keep an excessive amount of cash on hand or too many people with access to it due to the risk of petty cash theft and potential accounting problems. Petty cash is a current asset and should be listed as a debit on the company balance sheet. To initially fund a petty cash account, the accountant should write a check made out to “Petty Cash” for the desired amount of cash to keep on hand and then cash the check at the company’s bank.A petty cash fund is a convenient method to pay for small business transactions such as postage, delivery fees or emergency office supplies. It is important to keep accurate records of all petty cash expenditures for bookkeeping purposes.
