Allowance For Doubtful Accounts DefinitionRegardless of which percentage is used, either percentage would probably result in a reasonable estimate of uncollectible accounts receivable. Using the 1.70% estimate, the Nicholas Corporation would prepare the following journal entry to record uncollectible accounts expense in January. The uncollectible accounts expense account shows the company estimates it cost $750 in January to sell to customers who will not pay. The accounts receivable account shows the company’s customers owe it $50,000.
Let’s say you have a total of $50,000 in accounts receivable ($50,000 X 2%). The Nicholas Corporation could have easily obtained the above credit sales information from its general ledger. The total dollar amount of debits to accounts receivable represent credit sales. Similarly, the dollar amount of accounts receivable not collected could have been obtained through an analysis of the company’s accounts receivable subsidiary ledger.
Responses to “Adjusted Trial Balance”
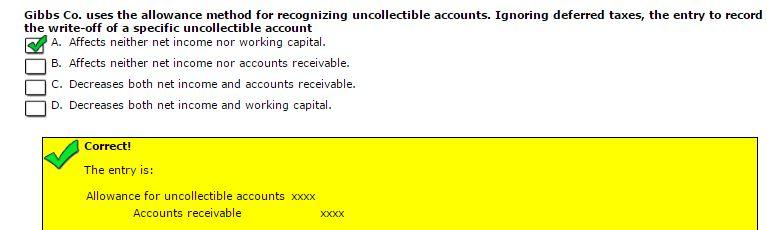
Inasmuch as it usually has a credit balance, as opposed to most assets with debit balances, the allowance for uncollectible accounts is called a contra asset account. The percentage of credit sales approach focuses on the income statement and the matching principle. Sales revenues of $500,000 are immediately matched with $1,500 of bad debts expense. The balance in the account Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is ignored at the time of the weekly entries. However, at some later date, the balance in the allowance account must be reviewed and perhaps further adjusted, so that the balance sheet will report the correct net realizable value.When a specific account is identified as uncollectible, the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts should be debited and Accounts Receivable should be credited. The allowance for doubtful accounts is a reduction of the total amount of accounts receivable appearing on a company’s balance sheet, and is listed as a deduction immediately below the accounts receivable line item. The allowance represents management’s best estimate of the amount of accounts receivable that will not be paid by customers.It does not necessarily reflect subsequent actual experience, which could differ markedly from expectations. If actual experience differs, then management adjusts its estimation methodology to bring the reserve more into alignment with actual results.
Is allowance for doubtful accounts the same as allowance for uncollectible accounts?
An allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra-asset account that nets against the total receivables presented on the balance sheet to reflect only the amounts expected to be paid. The allowance for doubtful accounts is only an estimate of the amount of accounts receivable which are expected to not be collectible.

The Importance Of Analyzing Accounts Receivable
Thus, the net impact of the provision for doubtful debts is to accelerate the recognition of bad debts into earlier reporting periods. When credit sales are made, the effect is an increase in resources (assets) and an increase in sources of resources (stockholders equity). The specific accounts affected are accounts receivable (debited) and sales (credited). When a company estimates that some of its accounts receivable are uncollectible, in effect it is saying some of its accounts receivable are not resources.
Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts Definition
The reserve is a contra-asset, or an asset listed on the balance sheet with a negative value meant to offset the value of accounts receivable. To record the reserve, you debit uncollectible accounts expense and credit allowance for uncollectible accounts. In addition to creating the reserve, this entry decreases business income for the year. When the allowance account is used, the company is anticipating that some accounts will be uncollectible in advance of knowing the specific account.Similarly, it is saying its sources of resources are too high because some credit sales will never result in resources, specifically cash. Remember, accounts receivable are not valuable if they do not eventually result in cash. In order to properly account for uncollectible accounts receivable, companies reduce their resources and sources of resources for estimated uncollectible accounts receivable. For example, if a company with $50,000 of January credit sales estimates that 1.5% of such sales will not be collected, it would be affected as follows. At the time credit sales are made, the specific customers who will not pay are unknown.Remember the total of all accounts in the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger equals the balance in accounts receivable in the general ledger. Both the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger and the accounts receivable account in the general ledger will be reduced when the company identifies the specific customers who will not pay. Allowance for uncollectible accounts is a contra asset account on the balance sheet representing accounts receivable the company does not expect to collect. When customers buy products on credit and then don’t pay their bills, the selling company must write-off the unpaid bill as uncollectible.
- Since the specific customers are not known, customer accounts in the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger can not be reduced.
- It is important to note why companies use the allowance for uncollectible accounts rather than simply using accounts receivable.
- At the time uncollectible accounts expense is estimated, accounts receivable can not be decreased immediately because the specific customers who will not pay are not known at that time.
Recording the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Allowance for uncollectible accounts is also referred to as allowance for doubtful accounts, and may be expensed as bad debt expense or uncollectible accounts expense. A portion of a company’s customers that buy products or services from the company on credit may not be able to pay the company for various reasons. You can estimate your company’s uncollectible accounts to determine the amount of money that you expect your customers will not be able to pay using the percentage of receivables method. The Nicholas Corporation could use the above data to estimate its uncollectible accounts receivable in year 4.It is important to note why companies use the allowance for uncollectible accounts rather than simply using accounts receivable. At the time uncollectible accounts expense is estimated, accounts receivable can not be decreased immediately because the specific customers who will not pay are not known at that time. Since the specific customers are not known, customer accounts in the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger can not be reduced. Thus, since the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger can not be reduced, accounts receivable in the general ledger can not be reduced or the two ledgers would not be in agreement.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts: Normal Balance
The allowance for uncollectible accounts shows the company expects its customers to be unable to pay $750 of the $50,000 they owe. Based on accounts receivable and the allowance for uncollectible accounts, the company would predict it could collect $49,250 ($50,000 – $750) from its credit customers. This knowledge of expected cash collections is very important for managers who must plan their cash expenditures. Even though its customers owe it $50,000, management would not plan on spending the full $50,000 because $750 will probably never be received.The above table shows customers owing $1,215 did not pay in year 2 or year 3 and are not expected to pay. Viewed another way, 1.35% ($1,215 / $90,000) of year 2 credit sales were uncollectible. U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles require a business to include a contingency on its balance sheet in recognition of future losses that are probable and can be reasonably estimated. Businesses use historical data to estimate how much to reserve for uncollectible accounts.Uncollectible accounts expense was debited in the above journal entry in order to recognize the expense of selling to some customers who will not pay. Since expenses decrease stockholders equity, and stockholders’ equity decreases with debits, uncollectible accounts expense was debited. The allowance for uncollectible accounts was credited because the company’s (resources) decreased.

The allowance for doubtful accounts
If the following accounting period results in net sales of $80,000, an additional $2,400 is reported in the allowance for doubtful accounts, and $2,400 is recorded in the second period in bad debt expense. The aggregate balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts after these two periods is $5,400. Use the percentage of bad debts you had in the previous accounting period and apply it to your estimate. For example, if 2% of your sales were uncollectible, you could set aside 2% of your sales in your ADA account.
Is allowance for uncollectible accounts a current asset?
Allowance for uncollectible accounts is a contra asset account on the balance sheet representing accounts receivable the company does not expect to collect. When customers buy products on credit and then don’t pay their bills, the selling company must write-off the unpaid bill as uncollectible.Thus, companies who sell on credit must either estimate the dollar amount of accounts receivable that will not be collected or they must wait until the customers who will not pay can be clearly identified. The sales method applies a flat percentage to the total dollar amount of sales for the period. For example, based on previous experience, a company may expect that 3% of net sales are not collectible. If the total net sales for the period is $100,000, the company establishes an allowance for doubtful accounts for $3,000 while simultaneously reporting $3,000 in bad debt expense.
How should investors interpret accounts receivable information on a company’s balance sheet?
For example, if the company had January credit sales of $15,000, it could estimate its uncollectible accounts receivable to be $210 ($15,000 x .014). The .014 is the average percentage of uncollectible accounts receivable during year 1 through year 3. The .017 reflects an expected increase in uncollectible accounts receivable from the 1.55% experienced in year 3.If the seller is a new company, it might calculate its bad debts expense by using an industry average until it develops its own experience rate. The provision for doubtful debts is the estimated amount of bad debt that will arise from accounts receivable that have been issued but not yet collected.
