Adjusted balance DefinitionFor example, if there were 12 general journal entries that involved cash, there should be 12 general ledger entries that involve cash. The final value for the general ledger is the amount that is included in the trial balance. In a dual entry accounting system, entries are made in debit and credit columns. Increases in assets — the things you own — and expenses are entered in the debit column, while liabilities — or things you owe — and revenues are entered in the credit column.
What Are Account Adjustments?
What are adjusted trial balances used for?
The adjusted trial balance is not part of the financial statements – rather, it is an internal report that has two purposes: To verify that the total of the debit balances in all accounts equals the total of all credit balances in all accounts; and.Adjusted balance is one of several methods that credit card companies use to calculate a cardholder’s finance charge. The latter is the fee charged when a cardholder carries a balance from month to month instead of paying the balance off in full by each month’s due date. Adjusting entries bring the accounts up to date, while closing entries reduce the revenue, expense, and dividends accounts to zero balances for use in recording transactions for the next accounting period.
Adjusting journal entries are recorded in a company’s general ledger at the end of an accounting period to abide by the matching and revenue recognition principles. In accrual accounting, revenues are entered when they are earned, not when you are paid, and expenses are entered when they are incurred, not when you pay them. Before the end of the accounting period, adjusting entries are made to bring the accounts up to date. For example, if you owe workers $900 and they have not been paid, you would debit salary expense for $900 and credit salaries payable for $900 to show the expense and liability you owe.
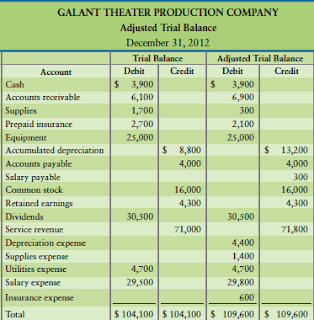
Examples of Adjusted Trial Balances
Income statement accounts that may need to be adjusted include interest expense, insurance expense, depreciation expense, and revenue. The entries are made in accordance with the matching principle to match expenses to the related revenue in the same accounting period. The adjustments made in journal entries are carried over to the general ledger which flows through to the financial statements. An adjusting journal entry is an entry in a company’s general ledger that occurs at the end of an accounting period to record any unrecognized income or expenses for the period.They are accrued revenues, accrued expenses, deferred revenues and deferred expenses. The purpose of adjusting entries is to convert cash transactions into the accrual accounting method. Accrual accounting is based on the revenue recognition principle that seeks to recognize revenue in the period in which it was earned, rather than the period in which cash is received. As an example, assume a construction company begins construction in one period but does not invoice the customer until the work is complete in six months. The construction company will need to do an adjusting journal entry at the end of each of the months to recognize revenue for 1/6 of the amount that will be invoiced at the six-month point.
Accounting Discussion Questions Chapter 3 & 4
Since the firm is set to release its year-end financial statements in January, an adjusting entry is needed to reflect the accrued interest expense for December. The adjusting entry will debit interest expense and credit interest payable for the amount of interest from December 1 to December 31. In summary, adjusting journal entries are most commonly accruals, deferrals, and estimates. Accruals are revenues and expenses that have not been received or paid, respectively, and have not yet been recorded through a standard accounting transaction. Deferrals refer to revenues and expenses that have been received or paid in advance, respectively, and have been recorded, but have not yet been earned or used.
Debits and Credits
Using the adjusted balance method gives consumers a grace period on new purchases because new purchases made in the current billing cycle aren’t added to the adjusted balance. This means the interest charge is not applied to those new balances, only to the balance at the end of the previous cycle minus any payments or credits. It also means that the adjusted balance method typically gives cardholders the lowest possible finance charge.
- An adjusting journal entry involves an income statement account (revenue or expense) along with a balance sheet account (asset or liability).
- It typically relates to the balance sheet accounts for accumulated depreciation, allowance for doubtful accounts, accrued expenses, accrued income, prepaid expenses,deferred revenue, and unearned revenue.
- Income statement accounts that may need to be adjusted include interest expense, insurance expense, depreciation expense, and revenue.
The trial balance is a business entity’s first attempt to balance its books when an accounting period ends. It takes the ending balances from each general ledger account. If done properly, the debit side of the trial balance will equal the credit side. If they don’t equal, then some investigation needs to happen to find the error so the accounting process can continue.
Why Is It Necessary to Complete an Adjusted Trial Balance?
Not all journal entries recorded at the end of an accounting period are adjusting entries. For example, an entry to record a purchase of equipment on the last day of an accounting period is not an adjusting entry. an entry made at the end of the accounting period that is used to record revenues to the period in which the earned and expenses to the period in which they occur. If you returned an item that cost $500 during the current billing cycle, the credit card company would credit this to your account to give you an adjusted balance of $3,000. Then, it would apply the finance charge to this balance instead of to the original $5,000.Accrued revenues are money earned in one accounting period but not received until another. Accrued expenses are expenses that are incurred in one accounting period but not paid until another. Deferred revenues are money that a business has been paid in advance for a service that will be provided later. Deferred expenses are expenses that have been paid in advance and will be expensed out at a later date.When a transaction is started in one accounting period and ended in a later period, an adjusting journal entry is required to properly account for the transaction. Adjusting journal entries can also refer to financial reporting that corrects a mistake made previously in the accounting period. Account adjustments are entries made in the general journal at the end of an accounting period to bring account balances up-to-date. They are the result of internal events, which are events that occur within a business that don’t involve an exchange of goods or services with another entity. There are four types of accounts that will need to be adjusted.
Free Debits and Credits Cheat Sheet
Estimates are adjusting entries that record non-cash items, such as depreciation expense, allowance for doubtful accounts, or the inventory obsolescence reserve. Any difference indicates that there is accounting error in the journal entries or in the ledger or in the calculations. With the adjusted balance method, every credit to your account will be subtracted before the credit card company assesses the finance charge. For example, say you had a balance of $5,000 at the end of the last billing cycle, and you made a payment of $1,500 during the current billing cycle. The company would subtract this payment, giving you an adjusted balance of $3,500.
Balance Sheets : Adjusting a Trial Balance Into a Classified Balance Sheet
The trial balance is the first attempt at balancing a business’ books at the end of an accounting period. As mentioned above, the trial balance is part of the accounting cycle and the correct sequence of accounting procedures. It’s compiled after all general journal entries have been posted to the general ledger and those totals have been computed.

An adjusting journal entry involves an income statement account (revenue or expense) along with a balance sheet account (asset or liability). It typically relates to the balance sheet accounts for accumulated depreciation, allowance for doubtful accounts, accrued expenses, accrued income, prepaid expenses,deferred revenue, and unearned revenue.
How do you fill out an adjusted trial balance?
The adjusted trial balance is an internal document that lists the general ledger account titles and their balances after any adjustments have been made. The adjusted trial balance is not a financial statement, but the adjusted account balances will be reported on the financial statements.If you had earned $100 interest from a bond, you would debit interest receivable for $100 and credit interest revenue for $100 to indicate the $100 you have coming, or receivable, and the revenue earned. The net effect of both journal entries have the same overall effect. Wages payable is zeroed out and wages expense is increased by $250. Making the reversing entry at the beginning of the period just allows the accountant to forget about the adjusting journal entries made in the prior year and go on accounting for the current year like normal. Reversing entries, or reversing journal entries, are journal entries made at the beginning of an accounting period to reverse or cancel out adjusting journal entries made at the end of the previous accounting period.
